Summary of this month
The temperature in most of the country's agricultural areas is close to normal or slightly higher; the central and eastern parts of the northwestern region, north-central North China, eastern Huanghuai, eastern Jianghuai, northwestern Jiangnan and southwestern regions have more than 30% to 1 times precipitation. The precipitation in the area is normal. Most of the northern agricultural areas have better light and temperature conditions, and the lyrical conditions are favorable for the growth and development of autumn harvest crops. However, heavy rainfall occurred in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, northwest and northeastern parts of the country, causing some farmland to suffer from heavy rains and floods. The warm water conditions of Jianghuai and Jianghan are basically conducive to crop growth and development. Most of the time in the south of the Yangtze River and South China is dominated by fine weather, which is conducive to early rice filling and mature harvesting, late rice seedling transplanting and greening growth; continuous high temperature in most parts of the south of the Yangtze River, strong precipitation in the central and northern parts of southern Jiangnan and southern South China. There is a certain adverse effect on the sun. The Sichuan Basin continues to be rainy and illuminating, with more precipitation, which is unfavorable for crop growth and development.
Weather and climate characteristics this month
Most of the country's agricultural areas have normal or slightly high temperatures, with temperatures ranging from 1 to 2 °C in the northwestern part of the Northeast, Jianghuai, eastern Jianghan, and northern Jiangnan (Figure 1). The highest temperature in most parts of the south of the Yangtze River is 10 to 21 days. High temperature ≥35°C. The monthly precipitation in most parts of the country is 100-250 mm (Fig. 2), including more precipitation in the central and eastern parts of the northwestern region, most of Inner Mongolia, north-central North China, eastern Huanghuai, eastern Jianghuai, northwestern Jiangnan and southwestern regions. 3 to 1 times; precipitation in most other areas is close to normal or slightly less (Figure 3). The sunshine in most parts of the country is basically close to the same period of the previous year, and only sunshine in Sichuan and Yunnan is less than 120 hours (Figure 4). 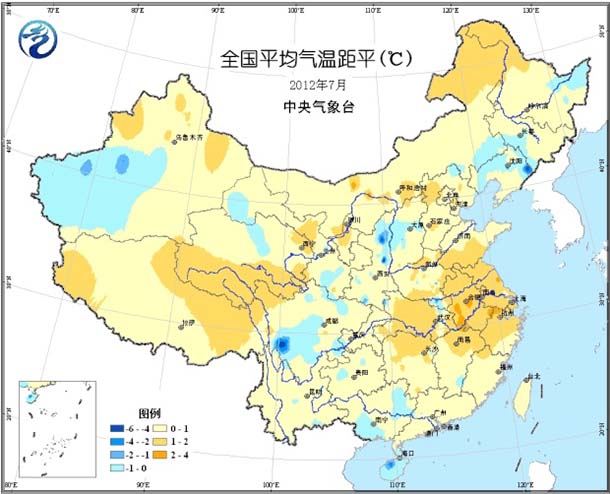
Figure 1 Average temperature anomaly in July 2012 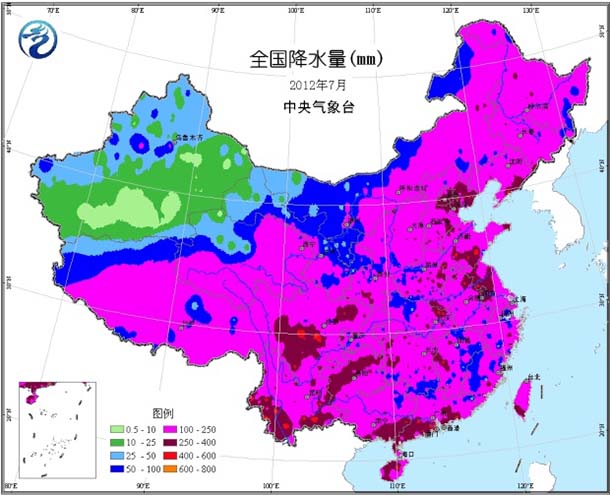
Figure 2 Cumulative precipitation in July 2012 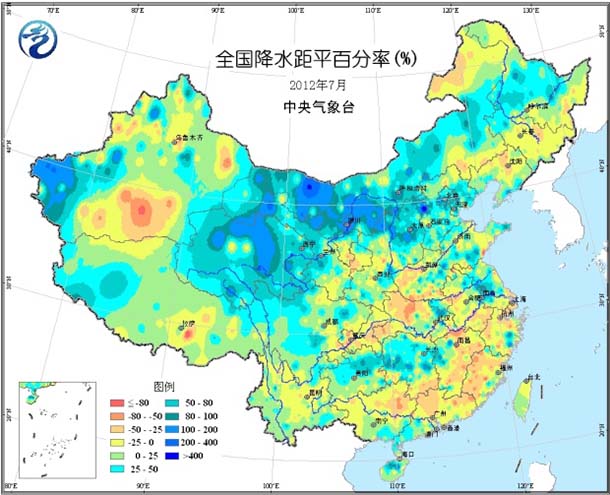
Figure 3 Percentage of precipitation anomalies in July 2012 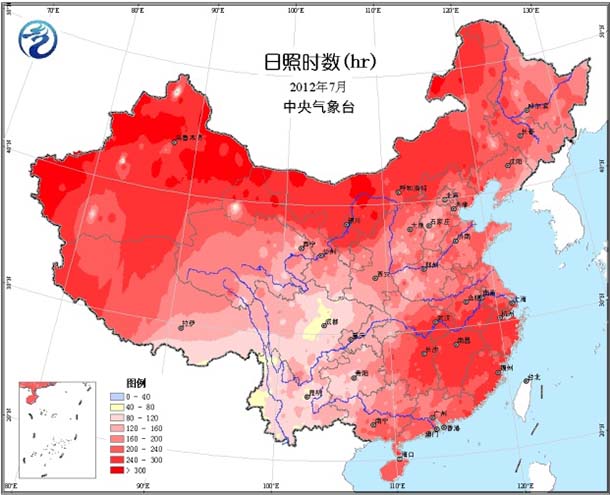
Figure 4 Cumulative sunshine hours in July 2012
Analysis of agricultural meteorological conditions in major agricultural areas this month
Northeast China, Inner Mongolia: Most of the northeastern region and Inner Mongolia have normal high temperature, abundant precipitation, and suitable soil moisture, especially in the middle and upper light conditions. It is beneficial to the jointing of corn, the flowering and pod formation of soybean, the rice seedling of the first season, and the forage grass growth in the pastoral area. The development of crops in most areas is close to normal. In the middle of Jilin Province, the precipitation in the southeast of Jilin Province and the southeastern part of Heilongjiang is more than 3 to 80%, and the temperature is lower than 1~2 °C. Especially in Jilin Yanbian Prefecture, the average daily temperature is lower than 15 °C on July 20, and there is a differentiation of the rice spikes in a season. Certain adverse effects.
Northwest, North China, Huanghuai: The light and temperature match is good in most of the month, and the farmland is suitable for the growth of crops. In the first half of the year, obvious precipitation occurred in most agricultural areas, and the drought in the early summer sowing area was relieved. In the latter part of the year, significant precipitation was conducive to further soil growth and agricultural storage. Heavy rains or heavy rains occurred in the central and eastern parts of North China and Northwest China. During the northern part of northern China, regional heavy rains and heavy rains occurred in the early part of northern China, causing soil wetland damage and accumulation in some farmland, and crop growth and development were adversely affected. Heavy rains and floods occurred in the area, causing crops such as corn and cotton to fall, farmland was flooded and destroyed, and agricultural production suffered heavy losses.
Jianghuai and Jianghan: Most of the temperature is 1~2°C higher than normal in the same period of the year. The light is sufficient, which is beneficial to the rice pupa, booting and cotton buds. From July 12 to 14, heavy precipitation occurred in most areas. The accumulated rainfall in some areas reached 100-200 mm. The wetland waterlogging in the eastern part of Jianghan and parts of the Jianghuai area was heavier, and even the farmland accumulated, causing the crops to fall and be flooded. In some seasons, the rice is slowly divided, the tillers are less, and the cotton buds are shed.
Jiangnan and South China: In the early and late stages of the south and the south and south of the south of the Yangtze River, the weather is normal and the light temperature is normal, which is conducive to early rice filling and mature early rice harvesting, late rice seedling transplanting and greening growth, and fruit tree fruit expansion and harvest. In the middle of the month, strong precipitation appeared in the middle and north of the Yangtze River, which was conducive to alleviating the high temperature in the early period, but delayed the early rice harvest and late rice transplanting, and the accumulated precipitation in some areas reached 100-250 mm, causing wetland damage in the farmland. In the second half of the year, the typhoon “Vicente†brought heavy storms to central and southern South China, and some areas suffered agricultural and fishery production losses. In the south of the Yangtze River, the highest temperature of ≥35 °C in 10 to 21 days is not conducive to the early grain filling and the growth of late rice seedlings, fruit trees and vegetables. Some early rice in Jiangxi and Hunan suffer from mild to moderate high temperature heat damage.
Southwest: Most of the precipitation in the eastern part of the southwestern region is more than 30% to 1 times, and there is less sunshine. Especially in the Sichuan Basin, most of the agricultural areas continue to be cloudy and rainy, which is not conducive to photosynthetic production of crops such as rice and corn in the first season; rainy, moderate temperature and high The wetness caused the rapid occurrence and spread of crop pests and diseases in Sichuan Basin and Guizhou. Heavy precipitation during the month also caused serious waterlogging disasters in farmland in the northeastern Sichuan Basin. In some areas, farmland was flooded and destroyed, and the effects of pest control were also adversely affected. The meteorological conditions in the southwestern part of the country are basically conducive to crop growth and development.
Major agricultural meteorological disasters this month
The national agrometeorological disasters are mainly rainstorms, winds, high temperature heat damage, low temperature chilling, pests and diseases, etc. (Figure 5).
Heavy rains and floods: heavy rainfall occurred in the southeastern part of the southwest, north-central Jiangnan, northern North China, southern South China, northeastern and northwestern parts of the country, and some areas experienced floods and floods, causing some farmland to be flooded and destroyed. Agricultural production suffered a large loss. From July 21 to 22, there were regional heavy rains in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei to the torrential rain. The heavy rain in Beijing was the strongest in the past 61 years, and Tianjin was the strongest in the past 34 years. The heavy rain caused a large flood disaster. The crops in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei were affected by 348 thousand hectares, of which corn was the most affected. According to incomplete statistics, the strong precipitation process on July 12-17 caused 259 thousand hectares of crops in Jiangxi and Hunan, and 38 kiloheals of harvest. In the latter part of the year, affected by the strong storms brought by the typhoon “Vicenteâ€, some of the early rice that has not yet been harvested in central and southern China will be flooded, bananas and sugar cane will be broken, and aquaculture will suffer some losses.
Popularity: affected by strong convective weather, Pingliang City, Gansu, Yulin, Baoji and Shangluo, Shaanxi, Erdos City, Inner Mongolia, Shijiazhuang, Zhangjiakou and Zhangzhou, Hebei, Taiyuan and Datong, Shanxi, Beichen District, Wuqing District and Qixian County, Beijing Pinggu District, Shandong Weifang, Dongying and Zibo City, Heilongjiang Harbin City, Liaoning Huludao City and Chaoyang Beipiao City, Chongqing Wuxi County, Guizhou Bijie City and Liupanshui City, Yunnan Kunming City and other places suffered from windstorms, resulting in local Plants such as corn are damaged and lodging, and vegetable greenhouses and livestock pens are destroyed. Among them, the winds and floods from July 21 to 22 caused 40,000 hectares of crops in Tianjin Beichen District, Wuqing District and Qixian County; and Yuzhong County, Huludao City, Liaoning Province, on July 22, thunderstorms and windy weather, crops affected by 9000 hectares.
High temperature heat damage: The high temperature of 10~21 days in the south of the Yangtze River has a high temperature of ≥35°C, which has an adverse effect on the early grain filling and the growth of late rice seedlings. Some of the early rice in Jiangxi and Hunan suffer from mild to moderate high temperature heat damage. The phenomenon of "high temperature ripening" appears. Continued hot weather has a certain adverse effect on the production of vegetables and melons.
Chilling damage: In the middle of the month, there are 2 to 4 days in eastern Jilin, where the average daily temperature is lower than 17 °C, and there is obstacle-type cold damage in rice. The average daily temperature in most of Yanbian Prefecture on July 20 is lower than 15 °C, and rice panicle differentiation is adversely affected. .
Pests and diseases: The precipitation in the eastern part of the southwestern part and the western part of the south of the Yangtze River is high, and the air humidity is high. The suitable temperature and long-term high-humidity field environment are conducive to the propagation and rapid spread of rice planthopper and rice leaf roller. The occurrence of rice planthopper and rice leaf roller in the Sichuan Basin, Guizhou and Hunan rice areas was heavier than last year; rice blast in Jilin City and Tonghua City in Jilin Province occurred more seriously. 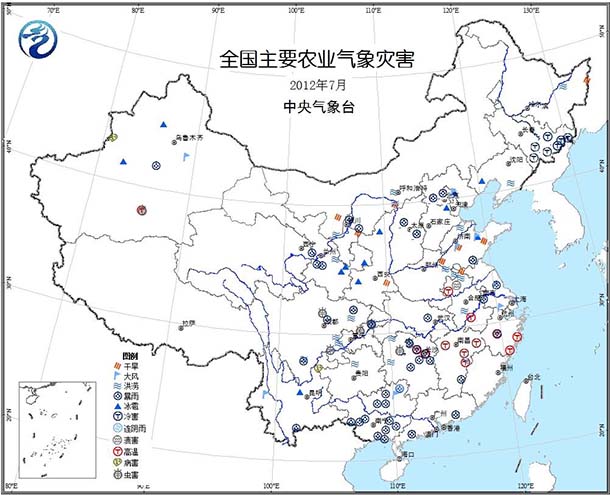
Figure 5 Agricultural meteorological disasters in July 2012
Outlook and recommendations for agricultural meteorological conditions this month
It is expected that in August, most of the country's temperature will be high and the precipitation will be abundant, which is conducive to the normal growth and development of autumn harvest crops. In the southern part of the Northeast, there is a lot of precipitation and the temperature is low, which may make the crop development process slower and weaker. Most of the North China and Huanghuai areas have more precipitation, and some areas may have wetland damage and flood disasters. The eastern part of North China and the northeastern part of Huanghuai may have staged rainy weather, which is not conducive to cotton flowering and ringing, corn ploughing and soybean Pod buds.
It is expected that in August, the temperature in the eastern part of Jianghan, the upper part of Jianghuai, and the northern part of the south of the Yangtze River will be 1 to 2 °C higher, the precipitation will be less, and there may be staged high temperature and drought, and the agricultural water may be insufficient. For the first season, the earing of the rice, the filling of the milk and the tillering of the late rice. Unfavourable booting, it is easy to cause cotton buds to fall off and the number of peaches to be reduced. The temperature in the south of South China is low and the precipitation is too high, which affects the photosynthetic growth of late rice, which may make the development of late rice slower. The precipitation in the northeastern part of the southwest is more than that, which is not conducive to the ripening and filling of rice in the first season, mature harvesting of spring corn and tobacco harvesting. . It is estimated that in August, there may be two or three tropical cyclones landing in China or seriously affecting coastal areas, and it is necessary to prevent its adverse effects on coastal agricultural and fishery production in China. Agricultural production advice:
The northern agricultural areas should strengthen water and fertilizer management, timely tillage and weeding, rational fertilization, and promote the vigorous growth of crops and yield formation; cotton fields should be pruned in time to improve the quality of cotton fiber and increase the number of peaches. Pay attention to the adverse effects of wet waterlogging and heavy rain and flood disasters on agricultural production in areas with excessive precipitation.
Jianghuai, Jianghan and Jiangnan strengthen the management of water and fertilizer in paddy fields. In high temperature areas, measures such as water temperature regulation and spraying of foliar fertilizer should be adopted to alleviate high temperature hazards. At the same time, management of dryland farmland such as corn and cotton should be strengthened, and water storage and protection should be paid attention to while preventing flooding. Defense against drought.
The southwestern region should use sunny weather or intermittent precipitation to timely harvest mature spring corn and tobacco leaves; areas with excessive precipitation should clear the ditch in time to improve the permeability of the field and promote the normal grain filling of crops such as rice.
All localities should pay attention to prevent the adverse effects of strong convective weather such as local windy hail and heavy rain caused by heavy rainfall on agricultural production, and strengthen the monitoring and control of pests and diseases; coastal areas should pay attention to the adverse effects of tropical cyclones on agricultural and fishery production.
Chain Link Gate,Chain Link,Black Chain Link Fence,Chain Link Fence Gate
Hebei Haiao Wire Mesh Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.haiaofence.com