Abstract : Particle size classification in synthetic diamond production; particle size inspection in quality inspection; and final determination of impact strength values ​​are inseparable from screening and screening machines. Screening involves screens, screens, screening parameters (such as feed rate, sieve time...). In order to obtain high-precision, reproducible, and efficient screening, all of the above factors must be considered. This paper reviews the origin of the screening technology; analyzes the problems existing in the current screening technology; and introduces the participation of foreign screening machines at the 2004 Shanghai Exhibition. In particular, the amount of feed for screening; the screening process arrangement; the standard screening for the requirements of the sieve machine, etc. Synthetic diamond is synthesized under high temperature and high pressure. It is a small crystal with a particle size ranging from one millimeter to several tens of micrometers. Synthetic diamonds are generally used as abrasives to further make abrasive tools or cutting tools. Diamond grinding tools or cutting tools are widely used in non-ferrous metal workpieces or in the processing of stone and concrete. Since the size of the abrasive particles is closely related to the processing efficiency and processing accuracy, an important process in the production of synthetic diamond is screening. By sieving, they are divided into several levels of different particle size ranges to meet the needs of different tools.
Screening involves screening screens, screening machines, screening parameters (such as feed rate, screening time), and the like. After clarifying their ins and outs, we hope to have a correct understanding of the screening and screening machines and correctly guide the screening parameters and the selection of the screening machine. 1. The origins and screens of screening technology In Greece and Rome in 150 BC, people began to use the "sieving" method to deal with the problems of daily life. In the 15th century, the Germans first began to weave the screen with a thread. And in 1867, the German professor P. R. Vun Rittinger suggests that the side length of the eyelet is increased or decreased by a ratio of √2 to form a series. In 1910, W.S. Tyler, Ine. first established a standard screen series with a ratio of "2". Since the two screens of adjacent particle size have a side length ratio of the mesh holes of √2, the woven mesh is a square eyelet. and so. The area ratio of the mesh holes of the two screens having the same particle size is "2". That is to say, the larger mesh area of ​​the adjacent screen is twice the area of ​​the smaller mesh. Taylor Corporation uses the number of meshes per square inch of area as the number of the screen (also known as mesh or "mesh"). If there are 200 meshes per square inch of area, the screen is called a 200 mesh (or 200 mesh) screen. The screen mesh was removed and the opening length of the 200 mesh screen was 0.0029 inches (0.07366 mm). Taylor uses a 200-mesh screen as the base. Thicker or finer screens are calculated on this basis in multiples of the √2 ratio. The larger the sieve number, the smaller the sieve opening. The screen size and mesh size of China's screens are consistent with the US and international standards ISO.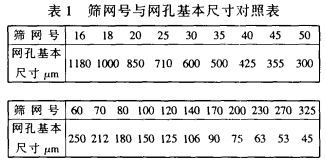
The screen commonly used in the synthetic diamond industry is a test sieve of 200. The marking of the test screen consists of the size of the screen frame, the basic dimensions of the screen holes, and the standard number. For example, the diameter of the screen frame is Ì„200mm; the height of the screen frame is 50mm; the basic size of the screen hole is 0.025mm; the standard is GB6003-85; and the screen number is 60, it is marked as +200x50/0.025GB6003-8560. 2. Particle size The particle size standard adopted by China's synthetic diamond industry is divided into two stages. Before the implementation of the national standard GB6003-85 "test sieve" in 1985, the screen title similar to the American Taylor company was used, such as 46 samples, 54 samples, 60 samples, and so on. After 1985, the national standard GB6003-85 is an ISO standard that directly adopts the International Organization for Standardization. This is a very good foundation for China's abrasive products to enter the international market. The national standard GB6003-85 stipulates that the particle size is determined by the nominal size of the meshes adjacent to the two screens. The particle size is named by the two screen numbers. Particles that pass through the 18-screen screen, such as through a 16-mesh screen, have a particle size of "16/18". This accurately defines the size range of the granularity. 3. Definition of sieving The solid granules are placed on a sieve surface having a certain pore size, and then the solid granules are rolled on the sieve surface; the sifting material is passed through the sieve holes; and the sieve material is trapped on the sieve surface. This classification method is called "screening." Simply put, “separate particles of different sizes with different sieves with different pore sizesâ€. During the sieving process, the necessary condition for the material to pass through the mesh is that the particle size must be smaller than the mesh size; at the same time, the particles have an opportunity to pass through the mesh. Some larger, unaided particles occupy the sieve opening position during sieving, so that the particles that pass through do not get the space through which they pass. Therefore, there must be some form of relative motion between the particles and the screen surface. In addition, since the amount of one feed is relatively large, there must be a certain screening time. This will allow the particles that can pass through to be sieved. 4. The plane running and the upper and lower movement of the screen have a certain form of relative movement between the sieved particles and the screen surface. The plane movement of the screen on the "slap-type vibrating screen" adopted by China's screening specification is It mimics the plane motion of human hand-screening things. Since some of the particles are irregular, they may leak halfway and not all pass; then it blocks the hole. If the crystals of this type have too many particles, they will occupy more holes. The particles that have been sieved down should not be allowed to leak. This requires removing the particles from the holes in the holes. "Slap" is also the role. Through the tapping of the weight, the mesh surface is vibrated up and down, and the sieved particles on the screen surface are bounced, and the particles half-clicked in the hole are bounced out. On the one hand, let out the eyelet; on the other hand, it may turn around and try other holes, maybe it will leak. 5. Screening parameters 5.1 Feeding quantity When making particle size inspections on single-size finished products, the national standards have been strictly regulated:
Table 2 Screening dosage at the time of particle size inspection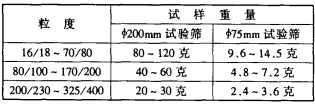
In the production of screening, a 4200 screen is generally used. The amount of feed is also used in an amount of 100 grams. What is the number of mesh holes in a 200mm screen? For a 200 mesh screen, there are 200 holes per square inch of area. The 4200 mesh area is approximately 48.68 square inches. Then the 2oo screen has 9738 holes, about 10,000. When the 200/300 particle size is detected, 20-30 grams of material is used. The 200mesh synthetic diamond has a particle size of about 40,000 per carat. Then the number of particles of 2030 g of synthetic diamond is: 40,000 × 5 × (2030) 14 million 2 million million mesh and the ratio of sieved particles: 1:1400-2100 to make 1,400-2,100 diamond particles pass through the same Screening holes. It is necessary to have a certain screening time!
Table 3 Ratio of sieve mesh to sieved particle size during particle size inspection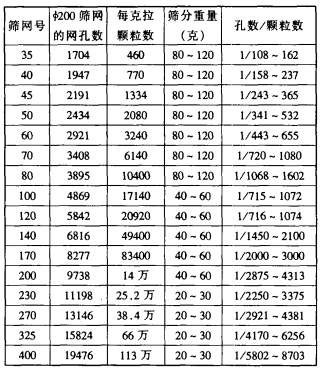
The amount of feed for production screening should be designed according to the particle size distribution obtained from the test to determine the amount of feed for the sieve. The percentage of each particle size of the diamond synthesized by different processes is different, that is, the particle size peak is different. If you can design the screen combination screen, the amount of feed and the screening time according to the "particle size peak"; consider the "ratio of the number of sieve holes to the number of sieved particles", you can get short screening time and screening accuracy. High effect. For example, the peak is at 50/60 and the weight ratio is about 50%. You can first sieve out 45 to the coarse screen. The amount: catch up, the time is shorter, and then put more screens from 50/60/70/80/loo... According to the particle size inspection, the feeding amount can be used to make the 50/60 moderate screening, and the finer sieve can be fully prepared! From the ratio of the number of holes per mesh of the q ̄2OOmm screen to the number of particles contained in the feed amount (see Table 3), the amount of feed specified by the national standard is unreasonable! If finer-grained sieving is appropriate, then sieving of coarser granules is a waste of time. Therefore, we still need to do meticulous work; further propose a reasonable screening amount. 5.2 Screening time The national standard specifies in the “particle size analysis†that the screening time is l5 minutes. In production, it usually takes 10 minutes to 15 minutes. Finer particle size screening also has a longer choice. From the ratio of the amount of feed to the number of mesh openings, it is known that each hole passes through an average of thousands of particles. Without a certain screening time guarantee, it is impossible to pass the particles that should pass. In addition, regardless of the particle size group and fineness, regardless of the number of particles, it is unreasonable to adopt a uniform screening time. It is a waste of time for coarser grains and insufficient screening for finer particles. 5.3 The speed and slap parameters of the sieve machine "Test method for particle size composition of synthetic diamond or cubic boron nitride" GB604.2-86, the speed of the sieve machine is 290 rpm; the number of slaps is 156 times per minute; The height of the drop between the beater and the soft plug is 38 ± 6 mm. It should be said that these three parameters are related to the movement of the sieved particles on the screen surface, and whether the particles trapped in the mesh can be ejected. But it is very rigorous! It only lists several surface parameters of the so-called "standard vibrating screen", and some essential problems are not limited. The screen on the vibrating screen is actually doing elliptical motion. The distance between the two focal points of the elliptical trajectory (that is, the two rotary axes) is important for sieving. If the distance is zero, it becomes a circular motion, and the sieved particles are only subjected to centrifugal force, and it is impossible to achieve screening at all. There is no limit to the problem of the slap parameter and the weight of the slapper. The slaps at the same slap height can produce very different forces from different slaps. 5.4 The problem of the slap-type vibrating screen The purpose of the slap is to make the particles of the screen vibrate. Avoid blocking the screen. Why can you shake up! That is, under the strong vibration of the slap, the screen produces up and down vibration like the drumhead. Thereby the particles on the screen are bounced. The up and down vibration of the screen means that the wire of the woven screen which has been fixed around it is elastically deformed; it means the deformation of the screen hole. When the sieve hole vibrates, it is small and small; although the deformation amount may not be large, it is not negligible for a fine mesh screen. In practice, when the screening is finished, the screen is removed, and when the screen frame is tapped on the side of the hand, it is often possible to sieve down. And as long as you shoot hard, you can always shoot. This is because the side of the screen frame slams the screen frame, and the screen hole also follows the deformation. It should be said that this is not standardized with respect to the screening principle. How can it be tolerated when the mesh hole is large and small? In summary, there are many problems with our screening national standards. We need to face it and try to fix it. 6. Development of sieve machine 6.1 tapping shaker American Ro-Tap Screening Machine
American Ro-Tap Screening Machine 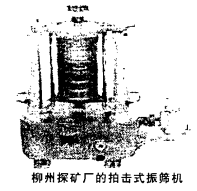
Slap-type vibrating screen machine of Liuzhou Prospecting Plant
The slap-type vibrating screen machine is the main screening equipment in China's synthetic diamond industry. For decades, most manufacturers have adopted this "standard" device. However, its structural disadvantages, such as fuel tank oil leakage; wear of mechanical rotating parts; especially the noise and screening mechanism defects, have caused many people to have the idea of ​​life. 6.2 The modification of the slap-type vibrating screen The principle is exactly the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen. Just replace the original worm gear, worm and fuel tank with belt drive and deceleration. The noise is still very large; the mechanical wear is more serious and the maintenance workload is large. 6.3 top impact vibrating screen machine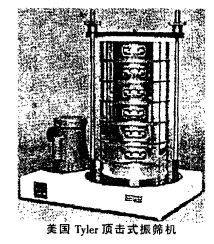
American Rryler top impact vibrating machine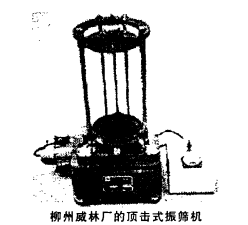 Its structural characteristics are basically the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen machine, except that the slap mechanism is cut off, and the whole set of screens that are clamped on the sieve machine are topped up, and then suddenly put down. Thereby, the screened object on the screen is moved up and down. Relative to the slap mechanism, it is more reasonable in principle. Although there are many manufacturers, there are not many adopters. The noise is still relatively large. 6.4 Plane rotation and electromagnetic vibration The composite screen shaker uses mechanical flat screen to rotate; then an electromagnet is used to attract the screen tray for up and down movement. It is large in size and its use is not ideal. Not widely accepted by the market. 6.5 Cyclone Wind Screener This is a sieve machine made in Germany. Its screen is made simple; compressed air blows the screened material into the screen. Under the action of a spiral blade agitator, it is pressed against the screen; the through-screen is the under-mattered material, and the unpermeable axial direction is blown out. The efficiency of such a screen machine is very high, but only one particle size can be screened at a time or in one machine. Only used by individual manufacturers. 6.6 Ultrasonic vibrating screen Install an ultrasonic transducer on the screen frame of the screen. The energy of the ultrasonic waves is used to vibrate the screen and pass it to the screened particles. Such a sieve machine has a high production efficiency when sieving a fine particle size (for example, 200 is fine), and has been adopted by a few manufacturers. 6.7 Electromagnetic Vibrating Screen Machine The ES-03 electromagnetic vibrating screen machine produced by Shenzhen Ruicheng Co., Ltd. adopts a special elastic system to generate vibration by electromagnetic driving. It allows the screened material to not only achieve vertical movement, but also to perform a rotary motion over the entire screen surface. Since the electromagnetic vibration frequency is high (3000 times per minute), it allows the sieved material particles to be present on most of the mesh holes in the shortest time, so that faster and more efficient screening can be obtained. The special setting of the intermittent vibration mode makes the upward movement of the acceleration higher when the sieve machine vibrates suddenly, and the particles blocked in the mesh can be vibrated to avoid the possibility of being blocked. In addition to the high vibration frequency, high screening efficiency, and the ability to keep the screen holes clean, it also has no mechanical wear problems; the screen has a long service life; the noise is very low; the weight is light; no need to hit the anchor screws, put on the table There are many advantages to working on it. It is being adopted by more and more users. 7 Status of foreign laboratory screening machines In early September 2004, Shanghai New International Expo Center held the Analytiea China 2004 Analytical Biochemical Exhibition. Mainly exhibited analysis, biochemical technology, laboratory technology equipment, etc., at the exhibition, six companies exhibited their screening machines. One treatment surface, which shows the mainstream trend of international laboratory sieve machines; on the other hand, it also shows their good market expectations for China. 8. Conclusion “Sieving†is a technique that is of low concern in the production of superhard materials; but it is also an essential and fundamental technology with some problems. Through analysis, we realized that the current screening amount is unreasonable; the slap noise of the slap-type vibrating screen; and the slap-type forced sieving should be and can be improved. From the progress of international screening technology, electromagnetic vibrating screen is a good alternative. The electromagnetic vibrating screen machine is adopted, and the feeding amount is fully considered, which will greatly reduce the noise level during the screening operation and improve the working environment; and the effects of good screening precision, high efficiency, and long service life of the screen can be obtained.
Its structural characteristics are basically the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen machine, except that the slap mechanism is cut off, and the whole set of screens that are clamped on the sieve machine are topped up, and then suddenly put down. Thereby, the screened object on the screen is moved up and down. Relative to the slap mechanism, it is more reasonable in principle. Although there are many manufacturers, there are not many adopters. The noise is still relatively large. 6.4 Plane rotation and electromagnetic vibration The composite screen shaker uses mechanical flat screen to rotate; then an electromagnet is used to attract the screen tray for up and down movement. It is large in size and its use is not ideal. Not widely accepted by the market. 6.5 Cyclone Wind Screener This is a sieve machine made in Germany. Its screen is made simple; compressed air blows the screened material into the screen. Under the action of a spiral blade agitator, it is pressed against the screen; the through-screen is the under-mattered material, and the unpermeable axial direction is blown out. The efficiency of such a screen machine is very high, but only one particle size can be screened at a time or in one machine. Only used by individual manufacturers. 6.6 Ultrasonic vibrating screen Install an ultrasonic transducer on the screen frame of the screen. The energy of the ultrasonic waves is used to vibrate the screen and pass it to the screened particles. Such a sieve machine has a high production efficiency when sieving a fine particle size (for example, 200 is fine), and has been adopted by a few manufacturers. 6.7 Electromagnetic Vibrating Screen Machine The ES-03 electromagnetic vibrating screen machine produced by Shenzhen Ruicheng Co., Ltd. adopts a special elastic system to generate vibration by electromagnetic driving. It allows the screened material to not only achieve vertical movement, but also to perform a rotary motion over the entire screen surface. Since the electromagnetic vibration frequency is high (3000 times per minute), it allows the sieved material particles to be present on most of the mesh holes in the shortest time, so that faster and more efficient screening can be obtained. The special setting of the intermittent vibration mode makes the upward movement of the acceleration higher when the sieve machine vibrates suddenly, and the particles blocked in the mesh can be vibrated to avoid the possibility of being blocked. In addition to the high vibration frequency, high screening efficiency, and the ability to keep the screen holes clean, it also has no mechanical wear problems; the screen has a long service life; the noise is very low; the weight is light; no need to hit the anchor screws, put on the table There are many advantages to working on it. It is being adopted by more and more users. 7 Status of foreign laboratory screening machines In early September 2004, Shanghai New International Expo Center held the Analytiea China 2004 Analytical Biochemical Exhibition. Mainly exhibited analysis, biochemical technology, laboratory technology equipment, etc., at the exhibition, six companies exhibited their screening machines. One treatment surface, which shows the mainstream trend of international laboratory sieve machines; on the other hand, it also shows their good market expectations for China. 8. Conclusion “Sieving†is a technique that is of low concern in the production of superhard materials; but it is also an essential and fundamental technology with some problems. Through analysis, we realized that the current screening amount is unreasonable; the slap noise of the slap-type vibrating screen; and the slap-type forced sieving should be and can be improved. From the progress of international screening technology, electromagnetic vibrating screen is a good alternative. The electromagnetic vibrating screen machine is adopted, and the feeding amount is fully considered, which will greatly reduce the noise level during the screening operation and improve the working environment; and the effects of good screening precision, high efficiency, and long service life of the screen can be obtained.
Screening involves screening screens, screening machines, screening parameters (such as feed rate, screening time), and the like. After clarifying their ins and outs, we hope to have a correct understanding of the screening and screening machines and correctly guide the screening parameters and the selection of the screening machine. 1. The origins and screens of screening technology In Greece and Rome in 150 BC, people began to use the "sieving" method to deal with the problems of daily life. In the 15th century, the Germans first began to weave the screen with a thread. And in 1867, the German professor P. R. Vun Rittinger suggests that the side length of the eyelet is increased or decreased by a ratio of √2 to form a series. In 1910, W.S. Tyler, Ine. first established a standard screen series with a ratio of "2". Since the two screens of adjacent particle size have a side length ratio of the mesh holes of √2, the woven mesh is a square eyelet. and so. The area ratio of the mesh holes of the two screens having the same particle size is "2". That is to say, the larger mesh area of ​​the adjacent screen is twice the area of ​​the smaller mesh. Taylor Corporation uses the number of meshes per square inch of area as the number of the screen (also known as mesh or "mesh"). If there are 200 meshes per square inch of area, the screen is called a 200 mesh (or 200 mesh) screen. The screen mesh was removed and the opening length of the 200 mesh screen was 0.0029 inches (0.07366 mm). Taylor uses a 200-mesh screen as the base. Thicker or finer screens are calculated on this basis in multiples of the √2 ratio. The larger the sieve number, the smaller the sieve opening. The screen size and mesh size of China's screens are consistent with the US and international standards ISO.

The screen commonly used in the synthetic diamond industry is a test sieve of 200. The marking of the test screen consists of the size of the screen frame, the basic dimensions of the screen holes, and the standard number. For example, the diameter of the screen frame is Ì„200mm; the height of the screen frame is 50mm; the basic size of the screen hole is 0.025mm; the standard is GB6003-85; and the screen number is 60, it is marked as +200x50/0.025GB6003-8560. 2. Particle size The particle size standard adopted by China's synthetic diamond industry is divided into two stages. Before the implementation of the national standard GB6003-85 "test sieve" in 1985, the screen title similar to the American Taylor company was used, such as 46 samples, 54 samples, 60 samples, and so on. After 1985, the national standard GB6003-85 is an ISO standard that directly adopts the International Organization for Standardization. This is a very good foundation for China's abrasive products to enter the international market. The national standard GB6003-85 stipulates that the particle size is determined by the nominal size of the meshes adjacent to the two screens. The particle size is named by the two screen numbers. Particles that pass through the 18-screen screen, such as through a 16-mesh screen, have a particle size of "16/18". This accurately defines the size range of the granularity. 3. Definition of sieving The solid granules are placed on a sieve surface having a certain pore size, and then the solid granules are rolled on the sieve surface; the sifting material is passed through the sieve holes; and the sieve material is trapped on the sieve surface. This classification method is called "screening." Simply put, “separate particles of different sizes with different sieves with different pore sizesâ€. During the sieving process, the necessary condition for the material to pass through the mesh is that the particle size must be smaller than the mesh size; at the same time, the particles have an opportunity to pass through the mesh. Some larger, unaided particles occupy the sieve opening position during sieving, so that the particles that pass through do not get the space through which they pass. Therefore, there must be some form of relative motion between the particles and the screen surface. In addition, since the amount of one feed is relatively large, there must be a certain screening time. This will allow the particles that can pass through to be sieved. 4. The plane running and the upper and lower movement of the screen have a certain form of relative movement between the sieved particles and the screen surface. The plane movement of the screen on the "slap-type vibrating screen" adopted by China's screening specification is It mimics the plane motion of human hand-screening things. Since some of the particles are irregular, they may leak halfway and not all pass; then it blocks the hole. If the crystals of this type have too many particles, they will occupy more holes. The particles that have been sieved down should not be allowed to leak. This requires removing the particles from the holes in the holes. "Slap" is also the role. Through the tapping of the weight, the mesh surface is vibrated up and down, and the sieved particles on the screen surface are bounced, and the particles half-clicked in the hole are bounced out. On the one hand, let out the eyelet; on the other hand, it may turn around and try other holes, maybe it will leak. 5. Screening parameters 5.1 Feeding quantity When making particle size inspections on single-size finished products, the national standards have been strictly regulated:
Table 2 Screening dosage at the time of particle size inspection

In the production of screening, a 4200 screen is generally used. The amount of feed is also used in an amount of 100 grams. What is the number of mesh holes in a 200mm screen? For a 200 mesh screen, there are 200 holes per square inch of area. The 4200 mesh area is approximately 48.68 square inches. Then the 2oo screen has 9738 holes, about 10,000. When the 200/300 particle size is detected, 20-30 grams of material is used. The 200mesh synthetic diamond has a particle size of about 40,000 per carat. Then the number of particles of 2030 g of synthetic diamond is: 40,000 × 5 × (2030) 14 million 2 million million mesh and the ratio of sieved particles: 1:1400-2100 to make 1,400-2,100 diamond particles pass through the same Screening holes. It is necessary to have a certain screening time!
Table 3 Ratio of sieve mesh to sieved particle size during particle size inspection

The amount of feed for production screening should be designed according to the particle size distribution obtained from the test to determine the amount of feed for the sieve. The percentage of each particle size of the diamond synthesized by different processes is different, that is, the particle size peak is different. If you can design the screen combination screen, the amount of feed and the screening time according to the "particle size peak"; consider the "ratio of the number of sieve holes to the number of sieved particles", you can get short screening time and screening accuracy. High effect. For example, the peak is at 50/60 and the weight ratio is about 50%. You can first sieve out 45 to the coarse screen. The amount: catch up, the time is shorter, and then put more screens from 50/60/70/80/loo... According to the particle size inspection, the feeding amount can be used to make the 50/60 moderate screening, and the finer sieve can be fully prepared! From the ratio of the number of holes per mesh of the q ̄2OOmm screen to the number of particles contained in the feed amount (see Table 3), the amount of feed specified by the national standard is unreasonable! If finer-grained sieving is appropriate, then sieving of coarser granules is a waste of time. Therefore, we still need to do meticulous work; further propose a reasonable screening amount. 5.2 Screening time The national standard specifies in the “particle size analysis†that the screening time is l5 minutes. In production, it usually takes 10 minutes to 15 minutes. Finer particle size screening also has a longer choice. From the ratio of the amount of feed to the number of mesh openings, it is known that each hole passes through an average of thousands of particles. Without a certain screening time guarantee, it is impossible to pass the particles that should pass. In addition, regardless of the particle size group and fineness, regardless of the number of particles, it is unreasonable to adopt a uniform screening time. It is a waste of time for coarser grains and insufficient screening for finer particles. 5.3 The speed and slap parameters of the sieve machine "Test method for particle size composition of synthetic diamond or cubic boron nitride" GB604.2-86, the speed of the sieve machine is 290 rpm; the number of slaps is 156 times per minute; The height of the drop between the beater and the soft plug is 38 ± 6 mm. It should be said that these three parameters are related to the movement of the sieved particles on the screen surface, and whether the particles trapped in the mesh can be ejected. But it is very rigorous! It only lists several surface parameters of the so-called "standard vibrating screen", and some essential problems are not limited. The screen on the vibrating screen is actually doing elliptical motion. The distance between the two focal points of the elliptical trajectory (that is, the two rotary axes) is important for sieving. If the distance is zero, it becomes a circular motion, and the sieved particles are only subjected to centrifugal force, and it is impossible to achieve screening at all. There is no limit to the problem of the slap parameter and the weight of the slapper. The slaps at the same slap height can produce very different forces from different slaps. 5.4 The problem of the slap-type vibrating screen The purpose of the slap is to make the particles of the screen vibrate. Avoid blocking the screen. Why can you shake up! That is, under the strong vibration of the slap, the screen produces up and down vibration like the drumhead. Thereby the particles on the screen are bounced. The up and down vibration of the screen means that the wire of the woven screen which has been fixed around it is elastically deformed; it means the deformation of the screen hole. When the sieve hole vibrates, it is small and small; although the deformation amount may not be large, it is not negligible for a fine mesh screen. In practice, when the screening is finished, the screen is removed, and when the screen frame is tapped on the side of the hand, it is often possible to sieve down. And as long as you shoot hard, you can always shoot. This is because the side of the screen frame slams the screen frame, and the screen hole also follows the deformation. It should be said that this is not standardized with respect to the screening principle. How can it be tolerated when the mesh hole is large and small? In summary, there are many problems with our screening national standards. We need to face it and try to fix it. 6. Development of sieve machine 6.1 tapping shaker
 American Ro-Tap Screening Machine
American Ro-Tap Screening Machine 
Slap-type vibrating screen machine of Liuzhou Prospecting Plant
The slap-type vibrating screen machine is the main screening equipment in China's synthetic diamond industry. For decades, most manufacturers have adopted this "standard" device. However, its structural disadvantages, such as fuel tank oil leakage; wear of mechanical rotating parts; especially the noise and screening mechanism defects, have caused many people to have the idea of ​​life. 6.2 The modification of the slap-type vibrating screen The principle is exactly the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen. Just replace the original worm gear, worm and fuel tank with belt drive and deceleration. The noise is still very large; the mechanical wear is more serious and the maintenance workload is large. 6.3 top impact vibrating screen machine

American Rryler top impact vibrating machine
 Its structural characteristics are basically the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen machine, except that the slap mechanism is cut off, and the whole set of screens that are clamped on the sieve machine are topped up, and then suddenly put down. Thereby, the screened object on the screen is moved up and down. Relative to the slap mechanism, it is more reasonable in principle. Although there are many manufacturers, there are not many adopters. The noise is still relatively large. 6.4 Plane rotation and electromagnetic vibration The composite screen shaker uses mechanical flat screen to rotate; then an electromagnet is used to attract the screen tray for up and down movement. It is large in size and its use is not ideal. Not widely accepted by the market. 6.5 Cyclone Wind Screener This is a sieve machine made in Germany. Its screen is made simple; compressed air blows the screened material into the screen. Under the action of a spiral blade agitator, it is pressed against the screen; the through-screen is the under-mattered material, and the unpermeable axial direction is blown out. The efficiency of such a screen machine is very high, but only one particle size can be screened at a time or in one machine. Only used by individual manufacturers. 6.6 Ultrasonic vibrating screen Install an ultrasonic transducer on the screen frame of the screen. The energy of the ultrasonic waves is used to vibrate the screen and pass it to the screened particles. Such a sieve machine has a high production efficiency when sieving a fine particle size (for example, 200 is fine), and has been adopted by a few manufacturers. 6.7 Electromagnetic Vibrating Screen Machine The ES-03 electromagnetic vibrating screen machine produced by Shenzhen Ruicheng Co., Ltd. adopts a special elastic system to generate vibration by electromagnetic driving. It allows the screened material to not only achieve vertical movement, but also to perform a rotary motion over the entire screen surface. Since the electromagnetic vibration frequency is high (3000 times per minute), it allows the sieved material particles to be present on most of the mesh holes in the shortest time, so that faster and more efficient screening can be obtained. The special setting of the intermittent vibration mode makes the upward movement of the acceleration higher when the sieve machine vibrates suddenly, and the particles blocked in the mesh can be vibrated to avoid the possibility of being blocked. In addition to the high vibration frequency, high screening efficiency, and the ability to keep the screen holes clean, it also has no mechanical wear problems; the screen has a long service life; the noise is very low; the weight is light; no need to hit the anchor screws, put on the table There are many advantages to working on it. It is being adopted by more and more users. 7 Status of foreign laboratory screening machines In early September 2004, Shanghai New International Expo Center held the Analytiea China 2004 Analytical Biochemical Exhibition. Mainly exhibited analysis, biochemical technology, laboratory technology equipment, etc., at the exhibition, six companies exhibited their screening machines. One treatment surface, which shows the mainstream trend of international laboratory sieve machines; on the other hand, it also shows their good market expectations for China. 8. Conclusion “Sieving†is a technique that is of low concern in the production of superhard materials; but it is also an essential and fundamental technology with some problems. Through analysis, we realized that the current screening amount is unreasonable; the slap noise of the slap-type vibrating screen; and the slap-type forced sieving should be and can be improved. From the progress of international screening technology, electromagnetic vibrating screen is a good alternative. The electromagnetic vibrating screen machine is adopted, and the feeding amount is fully considered, which will greatly reduce the noise level during the screening operation and improve the working environment; and the effects of good screening precision, high efficiency, and long service life of the screen can be obtained.
Its structural characteristics are basically the same as that of the slap-type vibrating screen machine, except that the slap mechanism is cut off, and the whole set of screens that are clamped on the sieve machine are topped up, and then suddenly put down. Thereby, the screened object on the screen is moved up and down. Relative to the slap mechanism, it is more reasonable in principle. Although there are many manufacturers, there are not many adopters. The noise is still relatively large. 6.4 Plane rotation and electromagnetic vibration The composite screen shaker uses mechanical flat screen to rotate; then an electromagnet is used to attract the screen tray for up and down movement. It is large in size and its use is not ideal. Not widely accepted by the market. 6.5 Cyclone Wind Screener This is a sieve machine made in Germany. Its screen is made simple; compressed air blows the screened material into the screen. Under the action of a spiral blade agitator, it is pressed against the screen; the through-screen is the under-mattered material, and the unpermeable axial direction is blown out. The efficiency of such a screen machine is very high, but only one particle size can be screened at a time or in one machine. Only used by individual manufacturers. 6.6 Ultrasonic vibrating screen Install an ultrasonic transducer on the screen frame of the screen. The energy of the ultrasonic waves is used to vibrate the screen and pass it to the screened particles. Such a sieve machine has a high production efficiency when sieving a fine particle size (for example, 200 is fine), and has been adopted by a few manufacturers. 6.7 Electromagnetic Vibrating Screen Machine The ES-03 electromagnetic vibrating screen machine produced by Shenzhen Ruicheng Co., Ltd. adopts a special elastic system to generate vibration by electromagnetic driving. It allows the screened material to not only achieve vertical movement, but also to perform a rotary motion over the entire screen surface. Since the electromagnetic vibration frequency is high (3000 times per minute), it allows the sieved material particles to be present on most of the mesh holes in the shortest time, so that faster and more efficient screening can be obtained. The special setting of the intermittent vibration mode makes the upward movement of the acceleration higher when the sieve machine vibrates suddenly, and the particles blocked in the mesh can be vibrated to avoid the possibility of being blocked. In addition to the high vibration frequency, high screening efficiency, and the ability to keep the screen holes clean, it also has no mechanical wear problems; the screen has a long service life; the noise is very low; the weight is light; no need to hit the anchor screws, put on the table There are many advantages to working on it. It is being adopted by more and more users. 7 Status of foreign laboratory screening machines In early September 2004, Shanghai New International Expo Center held the Analytiea China 2004 Analytical Biochemical Exhibition. Mainly exhibited analysis, biochemical technology, laboratory technology equipment, etc., at the exhibition, six companies exhibited their screening machines. One treatment surface, which shows the mainstream trend of international laboratory sieve machines; on the other hand, it also shows their good market expectations for China. 8. Conclusion “Sieving†is a technique that is of low concern in the production of superhard materials; but it is also an essential and fundamental technology with some problems. Through analysis, we realized that the current screening amount is unreasonable; the slap noise of the slap-type vibrating screen; and the slap-type forced sieving should be and can be improved. From the progress of international screening technology, electromagnetic vibrating screen is a good alternative. The electromagnetic vibrating screen machine is adopted, and the feeding amount is fully considered, which will greatly reduce the noise level during the screening operation and improve the working environment; and the effects of good screening precision, high efficiency, and long service life of the screen can be obtained.7+Person Hot Tub
7+ Person Hot Tub,large outdoor spa,outdoor living pool spa,spa with outdoor heated pool,modern outdoor hot tub
Guangzhou Aijingsi Sanitary Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.inspirationhottub.com