The coal-based activated carbon for desulfurization is made of high-quality coal and refined with advanced process equipment. The appearance is columnar particles or amorphous particles, has a large specific surface area, a suitable pore structure, high mechanical strength, can withstand high temperature, high pressure, is not easily broken, easy to regenerate, and has a long service life.

Desulfurized activated carbon
Coal-based activated carbon for desulfurization is widely used in flue gas desulfurization in thermal power plants, oil refining, petrochemical and chemical fiber industries, desulfurization of feedstock gas in chemical fertilizer industry, gas desulfurization in gas, natural gas desulfurization and other chemical industries, and is the best for producing carbon disulfide. additive.
Desulfurization activated carbon characteristics:
The appearance of this product is black columnar body, tasteless. The product uses anthracite as raw material, and the high-specific surface area of ​​carbon is activated by high temperature steam in the Slipper furnace, supplemented by special process and loaded into the catalyst. The product has good adsorption and decomposition effects on chemical gases such as hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide produced by chemical fertilizer plants and power plants, as well as chemical substances such as mercaptans remaining in gasoline and other chemical solvents.
Technical indicators: (Executive standard GB/T 7701.1-1997)
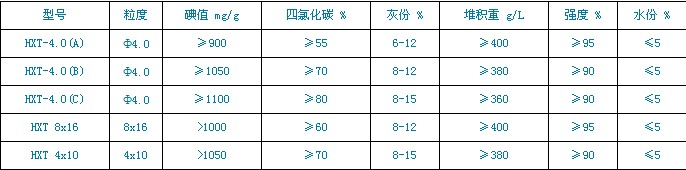
The desulfurized activated carbon is refined by physical activation method, which is black granular, non-toxic and tasteless, has large sulfur capacity, high desulfurization efficiency, good mechanical strength, small penetration resistance and easy regeneration. It is widely used in desulfurization of thermal power plants, petrochemicals, gas, natural gas and other gases.
Puyang Dixin Purification Material Factory is a comprehensive entity specializing in the production of water purifying agents, filter materials and fillers. It produces more than ten kinds of products, with advanced production technology and perfect testing methods, strong technical force and scientific management. The products are widely used in water treatment systems for electric power, chemical, metallurgy, gas, textile, printing and dyeing, petroleum and urban water supply and drainage industries.
The main products are: activated carbon, coal activated carbon, coconut shell activated carbon, wood powder activated carbon, shell activated carbon, special activated carbon for wine industry, activated carbon for purification water, coal columnar activated carbon, coal-based activated carbon for purifying air, coal-based activated carbon for desulfurization Coal-based activated carbon for recycling solvent, coal-based activated carbon for catalyst carrier, coal-based activated carbon for purifying water, carbon for purifying air, impregnated activated carbon, protective activated carbon, high-efficiency coconut shell gold, silver-shell shell activated carbon, apricot shell activated carbon, Pesticide hot activated carbon, petrochemical activated carbon, boiler raw water purification activated carbon, coconut shell gold activated carbon, MSG special activated carbon, spherical activated carbon and other activated carbon products.
Adsorption mechanism of activated carbon:
Activated carbon can be viewed as a material that provides an amazing surface area from millions of pores (equivalent to "sponges made up of molecules").
The process of enriching fluid molecules onto such surfaces by chemical and/or physical forces is referred to as "adsorption"; while "absorption" is the process by which a fluid molecule is absorbed and dispersed into a liquid or solid by a selected liquid or solid material. The process in the absorbent.
During the physical adsorption process, the adsorbate molecules are held on the surface of the activated carbon due to the weak van der Waals force (this force is generated by the attraction between the molecules), and the chemical structures of the activated carbon and the adsorbate are unchanged. In the chemisorption process, the adsorbate molecules react with the surface of the activated carbon (or the impregnating agent supported on the activated carbon surface) and are held by the activated carbon with a very strong chemical bonding force.
Usually, in order to achieve adsorption, the activated carbon must contain pores equivalent in size to the molecules to be adsorbed. The corresponding adsorption force generated by the surrounding pore walls to which the adsorbate molecules are adsorbed can reach a maximum value and should be greater than the energy level of the molecules.
For example, when decolorizing using microporous coconut shell activated carbon, the decolorizing ability is low because the coloring molecule or the pigment molecule is generally a large molecule and cannot enter the inside of the micropore via a channel having a smaller size than it. The coconut shell activated carbon has an excellent adsorption effect on small molecular substances. Another example is the rare gases æ°ª and æ°™ are easily adsorbed by coconut shell activated carbon, and are easily desorbed in macroporous charcoal such as wood activated carbon.
When the "liquid phase filling" of the adsorbate occurs inside the pores, the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon reaches the highest value. Under extremely high vapor pressure conditions, even within the mesopores (2.5 nm), "capillary condensation" (ie, "liquid phase filling") occurs due to multilayer adsorption of adsorbate.
In the constant temperature state, the "adsorption amount - adsorption pressure relationship diagram (for gas phase adsorption)" or "adsorption amount to concentration relationship diagram (for liquid phase adsorption)" is plotted, and the obtained curve is "(adsorption) isotherm".
For homologous chemicals, the amount of activated carbon adsorbed may increase with increasing pressure or with increasing molecular weight of adsorbate. Therefore, activated carbon adsorbs methane less than propane (more difficult to adsorb methane).
It is beneficial to remember this fact when designing a unique adsorption system that contains multiple adsorbate components.
After the adsorption adsorption system of the activated carbon adsorption system containing various adsorbate components is reached, it is often found that those adsorbents having a larger molecular weight are preferentially adsorbed components before all the adsorbates reach equilibrium. This phenomenon is called "competitive adsorption" or "preferential adsorption", and the first adsorbed small molecular weight substance is replaced by a subsequently adsorbed large molecular weight substance, and the former is re-desorbed from the surface of the adsorbent.
Physical adsorption occurring in the vapor phase can be affected by some external process parameters such as temperature and pressure. At lower temperatures and higher pressures, the adsorption efficiency is higher because the adsorption capacity of the adsorbate molecules is lower under such process conditions. This effect is also present in systems containing water and organic matter, which are easily adsorbed by the surface of the carbon, but when the organic matter preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the activated carbon arrives, the water molecules are desorbed in time. The reason for the occurrence of competitive adsorption is generally caused by the difference in molecular size, and the difference in molecular charge is also a cause of this phenomenon.
Generally speaking, the surface of activated carbon repels charged substances. Compared with most organic molecules, water is a highly charged substance (easy to ionize), so the adsorption of organic molecules by activated carbon takes precedence. The nitrogen atom of the primary amine compound is almost uncharged compared to the tertiary amine compound; the nitrogen atom charge of the tertiary amine compound is less than that of the secondary amine compound. Thus primary amines are more readily adsorbed by activated carbon than secondary amine compounds.
According to this prediction, activated carbon can adsorb higher levels of uncharged macromolecules; while those with high charge are not easily adsorbed by activated carbon.
The shape of the molecule also affects adsorption, but this is often considered a secondary factor.
For substances that can only be physically adsorbed by activated carbon at low levels (such as ammonia, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, mercury vapor, and methyl iodide), the effect of changes in operating conditions on the amount of adsorption can be ignored. To increase the amount of activated carbon adsorbed on these substances, a special compound (or its precursor substance) capable of chemically reacting with the adsorbate may be used to impregnate the activated carbon.
Since activated carbon contains a very large surface (activated carbon particles in a shoe with a surface area of ​​about 1/2 square mile!), the coated impregnant can be completely dispersed over such a large area, so the adsorbate molecules are impregnated. The probability of a compound capturing and reacting is extremely high. This mechanism of removing adsorbate is called "chemical adsorption."
Different from physical adsorption, the chemically adsorbed substances on the surface of activated carbon have undergone chemical structural changes, and it is no longer possible to desorb from the activated carbon in the original form of matter (the desorbed matter is not the original component, but Reaction product with an impregnating agent). This method has been applied to many industrial processes, especially in the field of industrial catalysis, and the ability to disperse catalytically active components onto the surface of activated carbon is greatly enhanced.
Note on the purchase of activated carbon:
1. Familiar with its indicators: The main adsorption indexes of activated carbon are: iodine adsorption value, carbon tetrachloride (CTC) adsorption value, methylene blue adsorption value, iodine adsorption value used to indicate the adsorption capacity of activated carbon for liquid substances, tetrachloro The carbon adsorption value is used to indicate the adsorption capacity of activated carbon for gaseous substances, and the methylene blue adsorption value is used to indicate the decolorization ability of activated carbon. The higher the three indexes, the stronger the adsorption capacity of activated carbon. Therefore, when purchasing activated carbon, you can choose the activated carbon suitable for your own use according to your own use and the indicators provided by the manufacturer.
2, understand its volume: the same 12 packs * 50g = 1 box Why Qiaobo activated carbon is larger than other homes? As already mentioned above, in order to improve the adsorption performance of activated carbon, only as much as possible on activated carbon Pore ​​structure, the more pores, the more loose the activated carbon, the lighter the relative density, so the good activated carbon feels lighter. In the case of the same weight package, the activated carbon will be much larger than the inferior activated carbon.
3. Master the ability of decolorization: Another performance of the adsorption capacity of activated carbon is the ability to decolorize. Activated carbon has the magical ability to turn colored liquids into light or colorless. This is actually because activated carbon adsorbs pigment molecules in colored liquids. Caused. Because of this characteristic of activated carbon, it is widely used in the production process of brown sugar to white sugar in the sugar industry. Take two transparent cups, put pure water in one cup, and then drop a drop of red ink (you can use any kind of pigment that is easy to observe but does not change the nature of the water, such as blue ink, printer color ink, However, you cannot use ink and carbon ink. After mixing, pour half of the colored water into another cup for comparison. Put the activated carbon into the colored water, the amount should reach half or more of the water, so the effect will be more obvious. After standing for 10-20 minutes, it is compared with the comparative water sample. Under the same conditions, the stronger the decolorization effect is, the adsorption of activated carbon is indicated. The better.
I believe that after you have seen these aspects, you will be very helpful in purchasing activated carbon in the future, and you will definitely choose your ideal product.
Aluminum Coil,Aluminum Coated Coil,Aluminum Roofing Material,Prepainted Aluminum Coil
SHAOXING YOTO IMPORT&EXPORT CO., LTD , https://www.sxyoto.com