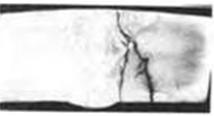
 Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): This is a general term used to refer to alloys that undergo stress in an aggressive environment due to the expansion of streak. Stress corrosion cracking has a brittle fracture morphology, but it can also occur in tough materials. The prerequisite for stress corrosion cracking is the presence of tensile stress (whether residual or applied stress, or both) and the presence of specific corrosive media. The formation and expansion of the pattern are approximately perpendicular to the tensile stress direction. The stress value that causes stress corrosion cracking is much lower than the stress value required for the material to break when no corrosive medium is present.
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): This is a general term used to refer to alloys that undergo stress in an aggressive environment due to the expansion of streak. Stress corrosion cracking has a brittle fracture morphology, but it can also occur in tough materials. The prerequisite for stress corrosion cracking is the presence of tensile stress (whether residual or applied stress, or both) and the presence of specific corrosive media. The formation and expansion of the pattern are approximately perpendicular to the tensile stress direction. The stress value that causes stress corrosion cracking is much lower than the stress value required for the material to break when no corrosive medium is present. Microscopically, a crack that passes through a grain is called a transgranular crack, and a crack that spreads along a grain boundary is called an intergranular crack. When stress corrosion cracking expands to a depth (here, the load-bearing material section When the stress reaches its fracture stress in air, the material breaks down as normal cracks (in ductile materials, usually through polymerization of microscopic defects).
Therefore, the section of the part that fails due to stress corrosion cracking will contain characteristic areas of stress corrosion cracking and "dendrite" areas associated with micro-defective polymerization.
Marble Look And Micro Crystal Tile
Marble Look And Micro Crystal Tile, Floor Tile,Rustic Tile,Glazed Tile
Roof Tile,Glazed Porcelain Tile Co., Ltd. , http://www.nbmosaictile.com