In CNC machine tools, the machine tool switching signal is usually controlled by a programmable controller (PLC). PLC has high reliability and is easy to use. However, in most CNC machine tools, especially economical CNC machine tools, the number of input and output points required is not much, usually below 60 points. Therefore, in order to reduce the cost of CNC machine tools, it can be used in CNC systems based on industrial PCs. The switch I/O board is connected with an external relay, and the machine software is used to control the machine tool switch. However, if the PC uses a single-tasking operating system (such as DOS), all tasks of the CNC system are placed in an overall message loop, the software is modular and maintainable, the risk of system failure is relatively concentrated, and can not Make full use of PC system resources. When using a non-real-time multi-tasking operating system (such as Windows), the design of Win32API does not take into account the development of real-time environment, the system call efficiency is not high, can not meet the real-time requirements of CNC system control.
To this end, this paper proposes an embedded PLC based on RT-Linux operating system, which utilizes RT-Linux's open, modular and extensible system structure features and multi-threaded/multi-tasking system environment to ensure real-time performance. At the same time, the risk of failure is relatively dispersed.
Hardware structure of CNC embedded PLC
The hardware of the CNC system is built on the open system of the general industrial PC. The embedded PLC hardware of the CNC system includes: industrial computer and its peripheral equipment, switch input and output interface card based on ISA bus, photoelectric isolation module and relay output module. Its structure is shown in Figure 1.
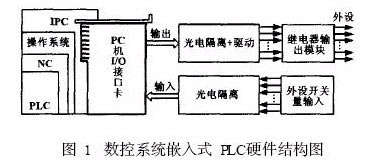
The industrial computer adopts RedHatLinux810+RTLinux311 operating system. The man-machine interface, numerical control code processing, trajectory planning, parameter management and PLC control of the numerical control system are realized by software through the industrial computer. No independent PLC controller is needed, and the numerical control system is reduced. The dependence of hardware helps to improve the openness of the system.
The I/O input and output information is exchanged between the host and the servo interface module and the I/O interface module through the PC I/O interface card. The PC I/O interface card is based on the ISA or PCI bus.
RT-Linux architecture
RT-Linux is a 32-bit hard real-time operating system based on Linux and running on a variety of hardware platforms.
It inherits the design philosophy of the MERT system, which is based on a general-purpose operating system and provides both real-time services in the strict sense and all standard POSIX services in the same operating system. The RT-Linux source code is open, easy to modify, and the system cost is reduced. The disclosure of the source code makes the development of the numerical control system free from the dependence on foreign software companies, and is conducive to improving the localization degree of the numerical control software.
RT-Linux is a multi-tasking real-time operating system based on Linux and running on multiple hardware platforms. By modifying the hardware layer of the Linux kernel, using interrupt simulation technology, a small and efficient real-time kernel is implemented between the kernel and the hardware, and a small real-time system is formed on the basis of the real-time kernel, and the Linux kernel is only used as a real-time system. The lowest priority task runs. For the general X86 hardware architecture, RT-Linux has excellent real-time performance and stability. The maximum interrupt latency is no more than 15μs, and the maximum task switching error is no more than 35μs. These real-time parameters are independent of the system load, and depend on the hardware of the computer. For example, on a normal PC with PII350 and 64M memory, the maximum delay time of the system is less than 1μs. RT-Linux is divided into real-time domain and non-real-time domain according to real-time performance. Its structure is shown in Figure 2.
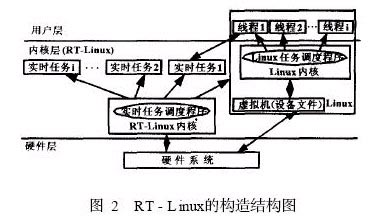
The real-time domain is designed to follow the design principles of real-time operating systems, that is, the system is transparent, modular, and scalable. The real-time kernel of RT-Linux consists of a core part and multiple optional parts. The core part is only responsible for high-speed interrupt processing, supports SMP operations and is not delayed or reentered by the underlying synchronization or interrupt routines. Other functions are augmented by dynamically loadable modules. RT-Linux leaves operations that do not affect the real-time nature of the system (ie, operations in non-real-time domains) to non-real-time Linux systems. Linux based on multi-tasking environment provides rich system resources for software development, such as multiple inter-process communication mechanisms and flexible memory management mechanisms.
Next page
Engineered Herringbone Wood Floors
Engineered Herringbone Wood Floors,Wood Classic Style,Wooden Flooring,Antique Oak Parquet Flooring
Shaoxing Haohua Timber Industry Co., Ltd. , https://www.woodtopiafloor.com