With the large-scale growth of the secondary battery market and the massive consumption of lithium resources, people began to seek alternatives to lithium batteries. Due to abundant sodium resources, low prices, and wide distribution, sodium ion batteries have gradually become one of the research hotspots in the field of energy storage. Since the standard potential of Na / Na + -2.71 V is close to the standard potential of Li / Li + -3.04 V, and the battery working principles of the two are similar, researchers can use the research and development experience in lithium ion batteries to apply to sodium ion batteries. However, the larger ion radius of sodium ions (Na +: 1.02 A vs Li +: 0.76 A) and slower kinetic rate make the commercial lithium ion battery anode material, graphite, as a negative electrode for sodium ion batteries unable to provide Satisfactory performance, so it is particularly important to develop a negative electrode material with a new structure for sodium ion batteries.
Recently, the Research Group of Photoelectric Conversion Materials and Devices of the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences has cooperated with Peking University and Zhejiang University to make new progress in the design of functionally oriented crystal structures and the preparation of new energy storage materials. The team prepared a new anode material Na2Cu2.09O0.50S2 based on the design concept of "structural functional area" and obtained excellent sodium ion storage performance. Na2Cu2.09O0.50S2 has a quasi-one-dimensional crystal structure, where the [Cu4S4] chain serves as an electronic conduction structural unit, making the sample conductivity as high as 0.5 S / cm; the Na4 [CuO] chain serves as an ion conducting structural unit, forming sodium aisle. The research team further reduced the grain size by ball milling, and finally achieved high specific capacity (588 mAh / g at 0.2 A / g), excellent rate performance (408 mAh / g at 2 A / g) and good Cycle performance (capacity retention rate after 400 cycles is 82%). The design idea based on "structural functional area" can provide new possibilities for the design and preparation of new electrode materials. Relevant research results were published in the international journal "Advanced Energy Materials" (Advanced Energy Materials 2019, DOI: 10.1002 / aenm.201900170) with the title Boosting the Stable Na Storage Performance in 1D Oxysulfide. The Shanghai Institute of Silicate and Zhejiang University jointly cultivated Ph.D. Graduate student Xu Jijian is the first author, and researcher Huang Fuqiang is the corresponding author.
The above research work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission.
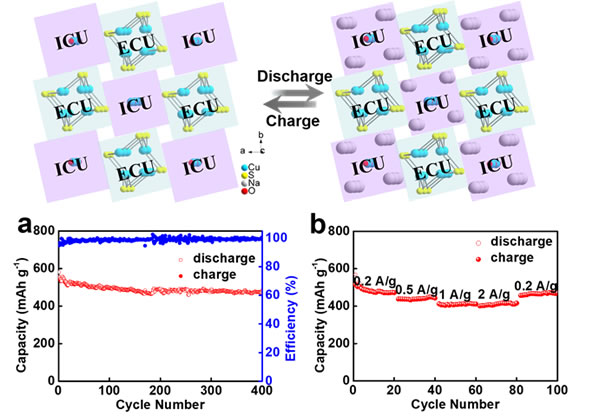
Schematic diagram of structure and function area and performance of sodium ion battery with Na2Cu2.09O0.50S2 anode material
Guangzhou Jointair Co., Ltd. , https://www.jointairaccessories.com